Artificial Rain Technology is also known as Cloud Seeding, enhances precipitation by dispersing substances like silver iodide or salt into clouds. This process encourages water droplets to coalesce and fall as rain. Typically conducted via aircraft or ground-based generators, cloud seeding targets specific weather conditions to maximize effectiveness. It plays a vital role in addressing water scarcity, supporting agriculture, and mitigating droughts. By artificially inducing rainfall, this technology helps sustain ecosystems and boosts food security, particularly in arid regions. However, its implementation requires careful monitoring and understanding of meteorological factors to achieve desired outcomes.
What is Artificial Rain Exactly?
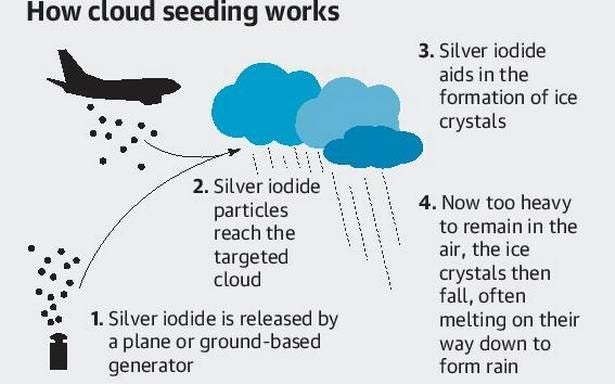
Artificial rain, commonly known as cloud seeding, is a scientific technique aimed at enhancing precipitation from clouds. It involves introducing hygroscopic or nucleating agents, such as silver iodide, sodium chloride, or potassium iodide, into the atmosphere to promote condensation and droplet formation within clouds.
Cloud seeding operates on the principle that cloud droplets need a nucleus—such as a particle of dust or a chemical agent—to form around. When these agents are introduced into supercooled cloud droplets, they can catalyze the aggregation of water molecules, resulting in larger droplets that eventually fall as precipitation.
The process can be conducted via aircraft or ground-based generators, targeting specific cloud systems that are already conducive to rainfall. While cloud seeding has shown promise in increasing precipitation rates, its efficacy can vary depending on environmental conditions, cloud type, and the presence of moisture. Ongoing research is focused on optimizing techniques and understanding the broader atmospheric implications of this intervention.
Why It’s Essential and Benifits:
- Water Scarcity: Many regions face water shortages due to climate change and population growth. Artificial rain can help alleviate these issues.
- Agricultural Support: It can boost crop yields by ensuring adequate water supply, which is crucial for food security.
- Drought Mitigation: It provides a tool for governments to combat prolonged droughts, helping to sustain ecosystems and economies.
- Flood Control: In some cases, artificial rain can redistribute rainfall patterns to prevent flooding in vulnerable areas.
Demerits of Artificial Rain Or Cloud Seeding:
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique aimed at increasing precipitation. While it has potential benefits, there are several drawbacks:
- Environmental Impact: The introduction of chemicals (like silver iodide) may have unknown effects on ecosystems and water sources.
- Efficacy: Results can be inconsistent; not all cloud types respond well to seeding, and it may not significantly increase rainfall.
- Cost: Cloud seeding operations can be expensive, with uncertain returns on investment.
- Ethical Concerns: Manipulating weather can lead to disputes over water rights, especially in areas where resources are already scarce.
- Dependence: Relying on artificial methods may detract from addressing the root causes of drought or water scarcity.
- Public Perception: There may be skepticism or opposition from communities concerned about potential health risks or environmental effects.
How It’s Achieved:
Cloud Seeding Materials: Common substances used include silver iodide, sodium chloride (table salt), and ice nuclei. These materials encourage water droplets in clouds to coalesce and fall as precipitation.
Methods:
- Aerial Seeding: Aircraft release seeding materials directly into clouds.
- Ground-Based Seeding: Ground-based generators can disperse materials into the atmosphere, allowing them to be carried up by wind.
- Weather Conditions: The technique is most effective when there are already suitable clouds present, and it usually requires specific atmospheric conditions.
Conclusion:
Artificial rain serves as a valuable tool in managing water resources, supporting agriculture, and addressing climate-related challenges. Its successful implementation relies on a combination of technology, meteorological understanding, and careful planning.
